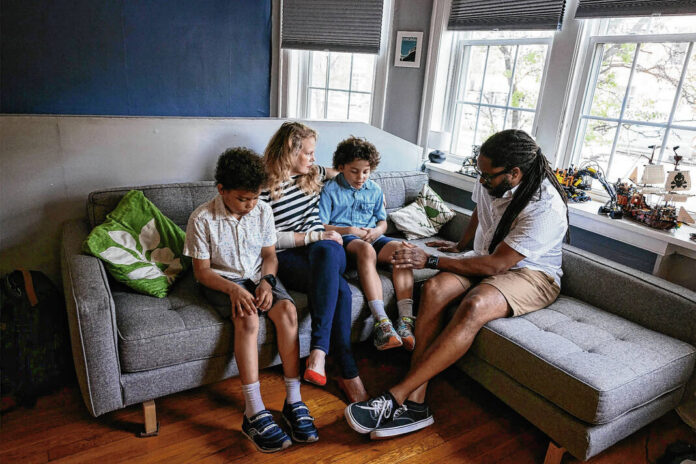
Allyson and Marcus Ward of Chicago moved across the country to be closer to family after the premature birth of their twins, Theo and Milo, left them with about $80,000 in medical debt. KHN and NPR’s reporting has revealed more than 100 million people in America are saddled with medical debt. (Taylor Glascock/NPR/Kaiser Health News/TNS)
Dozens of advocates for patients and consumers, citing widespread harm caused by medical debt, are pushing the Biden administration to take more aggressive steps to protect Americans from medical bills and debt collectors.
In letters to the IRS and the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau, the groups call for new federal rules that among other things would prohibit debt for medically necessary care from appearing on consumer credit reports.
Advocates also want the federal government to bar nonprofit hospitals from selling patient debt or denying medical care to people with past-due bills, practices that remain widespread across the U.S., KHN found.
And the groups are pressing the IRS to crack down on nonprofit hospital systems that withhold financial assistance from low-income patients or make aid cumbersome to get, another common obstacle KHN documented.
“Every day people are having to make choices about housing and clothing and food because of medical debt,” said Emily Stewart, executive director of Community Catalyst, a Boston nonprofit leading the effort. “It’s really urgent the Biden administration take action to put protections in place.”
Among the more than 50 groups supporting the initiative are national advocates such as the National Consumer Law Center, the Arthritis Foundation, and the Leukemia & Lymphoma Society.
Nationwide, 100 million people have health care debt, according to a KHN-NPR investigation, which has documented a crisis that is driving Americans from their homes, draining their savings, and preventing millions from accessing care they need.
While some of the debt appears on credit reports, much of it is hidden elsewhere as credit card balances, loans from relatives, or payment plans to hospitals and other medical providers.
The scale of this problem and its toll have spurred several national and state efforts.
Last spring, the White House directed federal agencies to work on relieving medical debts for veterans and to stop considering medical debt in evaluating eligibility for some federally backed mortgages.
California, Colorado, Maryland, New York, and other states have enacted new laws to expand consumer protections and require hospitals within their borders to increase financial aid. And the three largest credit agencies — Equifax, Experian, and Transunion — said they would stop including some medical debt on credit reports as of last July.
But many consumer and patient advocates say the actions, while important, still leave millions of Americans vulnerable to financial ruin if they become ill or injured. “It is critical that the CFPB take additional action,” the groups wrote to the federal agency created in 2010 to bolster oversight of consumer financial products.
The major credit rating companies, for example, agreed to exclude only debts that have been paid off and unpaid debts of less than $500. Patients with larger medical bills they can’t pay may still see their credit scores drop.
The groups also are asking the CFPB to eliminate deferred interest on medical credit cards. This arrangement is common for vendors such as CareCredit, whose loans carry no interest at first but can exceed 25% if patients don’t pay off the loan in time.
Collection industry officials have lobbied against broader restrictions on credit reporting, saying limits would take away an important tool that hospitals, physicians’ offices, and other medical providers need to collect their money and stay in business.
“We appreciate the challenges, but a broad ban on credit reporting could have some unintended consequences,” said Jack Brown III, president of Florida-based Gulf Coast Collection Bureau, citing the prospect of struggling hospitals and other providers closing, which would reduce care options.
Brown, a past president of ACA International, the collection industry’s leading trade association, warned that more medical providers would also start demanding upfront payment, putting additional pressure on patients.
To further protect patients from out-of-pocket costs like these, many advocates say hospitals, particularly those that are exempt from taxes because they are supposed to serve the community, must make financial aid more accessible, a key demand in the group’s letters. “For too long, nonprofit hospitals have not been behaving like nonprofits,” said Liz Coyle, executive director of the nonprofit Georgia Watch.
Charity care is offered at most U.S. hospitals. And nonprofit medical systems must provide aid as a condition of being tax-exempt. But at many medical centers, information about this assistance is difficult or impossible to find.
Standards also vary widely, with aid at some hospitals limited to patients with income as low as $13,590 a year. At other hospitals, people making five or six times that much can get assistance.
The result is widespread confusion that has left countless patients who should have been eligible for aid with large bills instead. A 2019 KHN analysis of hospital tax filings found that nearly half of nonprofit medical systems were billing patients with incomes low enough to qualify for charity care.
The groups are asking the IRS to issue rules that would set common standards for charity care and a uniform application across nonprofit hospitals. (Current regulations for charity care do not apply to for-profit or public hospitals.)
The advocates also want the federal agency to strengthen limits on how much nonprofit hospitals can charge and to curtail aggressive collection tactics such as foreclosing on patients’ homes or denying or deferring medical care.
More than two-thirds of hospitals sue patients or take other legal action against them, such as garnishing wages or placing liens on property, according to a recent KHN investigation. A quarter sell patients’ debts to debt collectors, who in turn can pursue patients for years for unpaid bills. About 1 in 5 deny nonemergency care to people with outstanding debt.
“Charitable institutions, which have other methods of collection available to them, should not be permitted to withhold needed medical care as a means to pressure patients to pay,” the groups wrote.
(KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.)
©2023 Kaiser Health News. Distributed by Tribune Content Agency, LLC.